Run Ollama on GPU in Ubuntu: Direct Installation & Docker Deployment Guide
I’ve been using Ollama on macOS for a while without issues, but recently noticed it was running on the CPU after switching to Ubuntu. At first, I thought it was out of VRAM—on macOS, Ollama automatically falls back to CPU if it runs out of memory. However, I found that Llama3.2 3B only uses 3GB of VRAM, which is far from exceeding limits. I checked the command line options but found no relevant settings, so I did some research.
Luckily, I found a blog explaining how to force GPU usage: run Ollama in a Docker container.
Updated on February 21, 2025
Thanks to two readers in the comments for pointing this out. After carefully checking the official documentation, I realized that while most official guides use containers, they don’t explicitly state that Linux only supports GPU acceleration via containers. I sincerely apologize for any confusion this oversight may have caused.
Before installing the Ollama container, I’ll explain how to verify if your system can run Ollama on GPU natively. You can decide whether to use containers based on your needs.
Direct Ollama Installation
Install Ollama
Installation is straightforward with a single command (use a mirror if the download is slow):
curl -fsSL https://ollama.com/install.sh | sh
Test it by installing any model (e.g., Llama3.2):
$ ollama run llama3.2 --verbose
>>> tell me a 100 words story
As the sun set over the ocean, Lena sat alone on the beach. She had just received
news that her grandmother, who had been her closest friend and confidant, had passed
away. Tears streamed down her face as she gazed out at the waves, feeling lost and
alone. But then she remembered the words of wisdom her grandmother had once shared:
"Life is like the tides, Lena. Sometimes it's calm, sometimes it's rough. But no
matter what, the beauty of the world will always be there." With a newfound sense of
peace, Lena let out a deep breath and smiled.
total duration: 1.64130885s
load duration: 56.215161ms
prompt eval count: 33 token(s)
prompt eval duration: 229ms
prompt eval rate: 144.10 tokens/s
eval count: 124 token(s)
eval duration: 1.354s
eval rate: 91.58 tokens/s
Verify GPU Usage in Ollama
You can roughly tell if Ollama is using the GPU from the generation speed, but here are more reliable methods:
Check Ollama’s Built-in Status
Run the following command to view Ollama’s process status:
$ ollama ps
NAME ID SIZE PROCESSOR UNTIL
llama3.2:latest a80c4f17acd5 4.0 GB 100% GPU About a minute from now
The “100% GPU” label indicates Ollama is configured to use the GPU, but it doesn’t confirm actual GPU utilization.
Confirm with nvidia-smi
To verify real-time GPU usage, run nvidia-smi with a 1-second refresh rate:
nvidia-smi -l 1
If GPU utilization and power consumption are at full load, Ollama is successfully using the GPU—congratulations!
What to Do If GPU Isn’t Being Used
If the GPU isn’t utilized, the issue likely occurs during GPU initialization. Try these fixes:
1. Reinstall Ollama with a Mirror
Sometimes GPU support fails due to network issues—Ollama downloads verification files during runtime, and failures prevent GPU initialization. Run ollama serve in the terminal to see error logs. Reinstall using a Gitee mirror to resolve network-related problems.
2. Follow Official Troubleshooting Steps
Refer to the official NVIDIA troubleshooting guide:

3. Fix nvidia_uvm Driver Issues
According to the official docs, suspending Ubuntu and resuming may cause Ollama to lose access to the NVIDIA GPU, forcing it to use the CPU. The official fix is to reload the nvidia_uvm module:
sudo rmmod nvidia_uvm && sudo modprobe nvidia_uvm
However, on desktop versions of Linux, you may encounter an “in use” error:
$ sudo rmmod nvidia_uvm && sudo modprobe nvidia_uvm
rmmod: ERROR: Module nvidia_uvm is in use
Resolve “Module in Use” Errors
- Check processes using the GPU with
nvidia-smi:
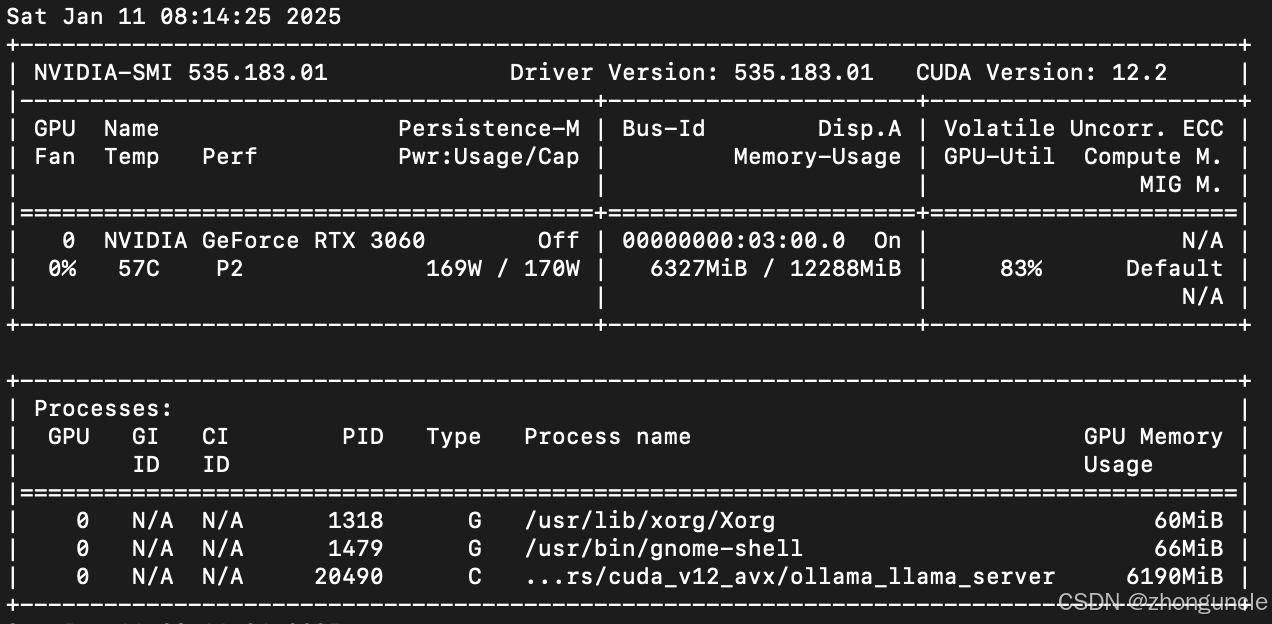
- Kill the processes (replace
PIDwith the actual process ID):sudo kill -9 PID
Desktop environments often restart these processes automatically, making it impossible to reload the driver. Server versions of Linux don’t have this issue.
If you can tolerate or resolve these driver issues, using the direct Ollama installation is more convenient. If not, use Docker for reliable GPU access.
Docker Container Deployment
Prerequisites
To run Ollama with GPU acceleration in Docker, you need:
- Docker Engine
- NVIDIA Container Toolkit (enables GPU support in containers)
If downloads are slow (e.g., for Ollama models or NVIDIA tools), switch your DNS to Alibaba Public DNS (223.5.5.5), restart your system, and wait a while for speeds to improve (I got full-speed downloads by afternoon).
Install Docker Engine
These steps install Docker Engine (command-line only) on Ubuntu/Debian. For Docker Desktop (GUI), search for separate guides. For other distributions, see the official Docker docs:
# Remove pre-installed Docker-related packages (if any)
for pkg in docker.io docker-doc docker-compose docker-compose-v2 podman-docker containerd runc; do sudo apt-get remove $pkg; done
# Add Docker's official GPG key
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install ca-certificates curl
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
# Add Docker repository to APT sources
echo \
"deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME") stable" | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt-get update
# Install Docker Engine
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin
Install NVIDIA Container Toolkit
Ensure you have NVIDIA GPU drivers installed first. For other distributions, refer to the official NVIDIA docs.
Installation Steps
# Add NVIDIA Container Toolkit GPG key and repository
curl -fsSL https://nvidia.github.io/libnvidia-container/gpgkey | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/nvidia-container-toolkit-keyring.gpg \
&& curl -s -L https://nvidia.github.io/libnvidia-container/stable/deb/nvidia-container-toolkit.list | \
sed 's#deb https://#deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/nvidia-container-toolkit-keyring.gpg] https://#g' | \
sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nvidia-container-toolkit.list
# Update APT and install the toolkit
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y nvidia-container-toolkit
Configuration
Configure Docker to use the NVIDIA runtime (run as root; see docs for non-root setup):
sudo nvidia-ctk runtime configure --runtime=docker
sudo systemctl restart docker
All prerequisites are now complete!
Deploy Ollama with GPU Acceleration
Step 1: Stop the Native Ollama Service
Ensure the native Ollama service is stopped to avoid port conflicts (Ollama uses port 11434 by default):
# Check for running Ollama processes
ps -A | grep ollama
# Kill the process (replace 1321 with your PID)
sudo kill 1321
Step 2: Run the Ollama Docker Container
Use this command to deploy Ollama with full GPU access:
docker run -d --gpus=all -v ./ollama:/root/.ollama -p 11434:11434 --name ollama ollama/ollama
Command explanation:
--gpus=all: Enable all available GPUs for the container.-v ./ollama:/root/.ollama: Mount the local./ollamadirectory to/root/.ollamain the container. This shares model files and resources (e.g., images for Llama3.2-Vision) between the host and container—no need to re-download models after container reinstallation.-p 11434:11434: Map container port 11434 (Ollama’s default port) to the host’s port 11434.--name ollama: Name the container “ollama” for easy management.ollama/ollama: Official Ollama Docker image name.
Step 3: Use Ollama in the Container
Enter the container’s command line:
sudo docker exec -it ollama /bin/bash
You can now use Ollama directly (no re-installation needed). Test with Llama3.1 8B:
ollama run llama3.1 --verbose
The
--verboseflag shows generation speed and performance metrics.
The model will download automatically. Once complete, you can start using Ollama:
root@b82bf49334f9:/# ollama run llama3.1 --verbose
pulling manifest
pulling 667b0c1932bc... 100% ▕███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▏ 4.9 GB
pulling 948af2743fc7... 100% ▕███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▏ 1.5 KB
pulling 0ba8f0e314b4... 100% ▕███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▏ 12 KB
pulling 56bb8bd477a5... 100% ▕███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▏ 96 B
pulling 455f34728c9b... 100% ▕███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████▏ 487 B
verifying sha256 digest
writing manifest
success
>>> 你好,请介绍一下你自己
大家好!我是 LLaMA,一个由 Meta 研发的语境理解和生成模型。我的主要功能是理解自然语言并根据上下文生成相关响应或内容。
total duration: 841.833803ms
load duration: 39.937882ms
prompt eval count: 17 token(s)
prompt eval duration: 5ms
prompt eval rate: 3400.00 tokens/s
eval count: 42 token(s)
eval duration: 795ms
eval rate: 52.83 tokens/s
>>> 你可以给我讲个故事吗
当然!这里有一个故事:
有一只小猴子名叫李莫,住在一个美丽的雨林里。他非常好奇,一天到晚都在探索周围的世界。有一天,他迷路了,找不到回家的路。
李莫沿着河流行走,希望能找到熟悉的地方。但是,无论他走多远,都不能见到熟悉的树木和花草。他开始感到害怕和孤独。
就在这时,他遇到了一个聪明的鸟儿。鸟儿问李莫:“你在哪里?你想去哪里?”李莫告诉了鸟儿自己的情况,鸟儿笑着说:“我知道这里的路
,你跟我走就可以找到回家的路。”
李莫和鸟儿一起行走,他们聊天、玩耍,这让小猴子觉得很开心。他慢慢地放下了担忧,感受到鸟儿的帮助和陪伴。
最后,他们来到一个熟悉的地方,小猴子看到家里熟悉的树木和花草,他高兴地冲向家门,鸟儿也跟着他一起欢笑。从那天起,李莫和鸟儿
成为好朋友,他们经常一起探索雨林里的秘密。
这个故事告诉我们,即使在迷路时,我们也可以寻找帮助和陪伴,而不是孤独地面对困难。
total duration: 6.86419438s
load duration: 35.787939ms
prompt eval count: 75 token(s)
prompt eval duration: 9ms
prompt eval rate: 8333.33 tokens/s
eval count: 306 token(s)
eval duration: 5.993s
eval rate: 51.06 tokens/s
GPU Utilization Verification
Docker uses a different architecture than traditional VMs—there’s no significant performance overhead. Check GPU usage with nvidia-smi (results may vary by model):

Restart the Container Later
After shutting down your system, restart the Ollama container with:
# Stop any running native Ollama processes first (if needed)
ps -A | grep ollama && sudo kill [PID]
# Start the existing container (do NOT use docker run—this creates a new container)
docker start ollama
Using docker run again will throw an error: “Unable to find image ‘ollama:latest’ locally”.
I’ll cover how to interact with the containerized Ollama from the host system in a future blog—this will include a comprehensive example using Llama3.2-Vision (which requires image sharing between the host and container).
I hope these will help someone in need~
References
- How to deploy the llama3 large model in CPU and GPU environments with Ollama - Gen. David L.: Where I learned about container-based GPU deployment.
- Ollama is now available as an official Docker image - Ollama: Official announcement stating Linux requires containers for GPU support (opposite of macOS, which needs the native app for GPU access).
- https://hub.docker.com/r/ollama/ollama - DockerHub: Official Ollama Docker image page.
- GPU - Ollama GitHub: Official Ollama documentation on GPU support.
- How to troubleshoot issues - Ollama GitHub: Official Ollama troubleshooting guide.